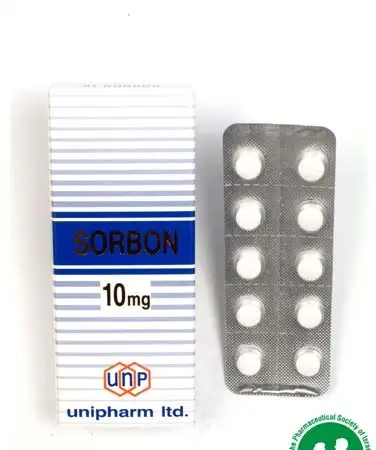
Buspirone is also known in Israel under the trade name Sorbon. It is a unique drug for the treatment of anxiety disorders. Many confuse it with common benzodiazepine drugs. However, it works by a different mechanism, and requires patience until you see the full effect. This drug is considered less addictive than benzodiazepines. In this comprehensive article, we will examine what buspirone is, how it works, what dosages are recommended, what the possible side effects are, and whether it is indeed a drug without a significant risk of addiction.
What is buspirone (Sorbonne)?
Buspirone It is an active ingredient that is classified as an anxiolytic. In Israel and other countries, it is sold under the name "Sorbon." This drug is different from benzodiazepines such as Xanax or Lorazepam, and it does not belong to the SSRI family such as Escitalopram or Zoloft.
Buspirone This drug was developed with the desire to offer treatment for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) without causing significant drowsiness or addiction like drugs from other families. Unlike benzodiazepines, this is not a drug with an immediate effect, but one that requires time to adapt until its positive effect is established. Therefore, those looking for a “quick” response to moments of acute anxiety may be disappointed, but those interested in long-term treatment will find that buspirone (Sorbonne) may be useful.
Sorbonne is also known as Buspirone HCl 10 mg, with the common dosage usually starting at 5 or 10 mg. People often ask: “what is buspirone?” or “is buspirone a controlled substance?” The answer is not simple for someone who is not knowledgeable in medicine. However, we will expand to explain that the drug is not classified as a controlled substance to the same degree of restriction as benzodiazepines. Therefore, it is not considered a “controlled substance” such as narcotic drugs.
What is buspirone used for?
Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
The primary use of buspirone is for Generalized Anxiety Disorder. People with GAD experience excessive and prolonged worry accompanied by feelings of tension, sleep disturbances, and unpleasant physical symptoms. Benzodiazepine medications are common, but they are considered to have a potential for addiction, withdrawal symptoms, and increased tolerance over time.
In contrast, Sorbonne is a slower-acting drug and does not cause an immediate feeling of calm. However, it excels in being less physically dependent. This is why many people prefer buspirone for the treatment of anxiety, especially for those who need consistent treatment over a period of time.
Advantages over other drugs
- Low addiction potential: Unlike benzodiazepines, buspirone has a lower risk of developing dependence.
- Mild side effects: Most often, its side effects are more subtle, mainly dizziness or mild nausea.
- Stable effect: There is no need to increase the dosage frequently to maintain effectiveness.
Buspirone for children
It is important to note that the use of buspirone in children requires careful medical evaluation. The available information suggests that it is less common in pediatrics than other ADHD or anxiety medications, but there may be cases where the pediatrician or psychiatrist will consider it. It is always advisable to consult a specialist before starting treatment in children.
How does buspirone work?
To the question "how does buspirone work?" or "buspirone mechanism of action," the answer is multifaceted. Buspirone affects the activity of neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly serotonin and dopamine.
Mechanism of action different from SSRIs and benzodiazepines
Although its effect involves serotonin receptors, buspirone does not inhibit reuptake like SSRIs, but rather acts as a partial agonist at 5-HT1A receptors. This mechanism leads to a reduction in overactivity of the serotonergic system, thereby reducing persistent feelings of anxiety.
Unlike benzodiazepines that act on GABA receptors, buspirone does not cause profound drowsiness or sharp changes in consciousness. As a result, effects such as immediate sedation or impairment of motor functions are relatively rare.
Gradual effect
Buspirone is known for its gradual onset of action. Patients may experience some improvement within a few weeks, but the full effect is often not felt until 4–6 weeks of consistent use. This is one of the main reasons why it is not recommended to take Sorbonne “as needed,” but rather as a regular medication.
Dosages and instructions for taking
Common dosages
Doctors usually start with a low dose of 5–10 mg per day (buspirone hcl 10 mg). The dose may be given twice a day or three times a day, depending on the doctor's instructions. In some cases, it can be gradually increased to a maximum dose of 60 mg per day, but these are exceptional situations in which the patient does not respond to low doses.
buspirone dosage
The dosage varies from person to person, taking into account age, weight, general health condition, and personal response to the medication. Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions. Doses of 15–30 mg per day are often common as an effective treatment for anxiety. Your doctor may gradually adjust the dosage until you achieve the best result with minimal side effects.
The importance of regular intake
Unlike benzodiazepines such as Xanax, buspirone should not be taken only during an acute anxiety attack. The drug must be taken daily for a period of time, as its effects gradually build up. Taking it regularly and at regular times helps to achieve a stable concentration level in the blood.
General guidelines
- Avoiding passing balls without consultation: There are tablets that are designed for controlled release, and they should not be broken.
- Taking with or without foodThere is no blanket guideline requiring taking with food, but it is best to maintain consistency in the way you take it to avoid changes in absorption.
- Avoiding alcohol: We will expand on this later, but it is not recommended to combine Buspirone and alcohol, as both may affect the central nervous system and produce unexpected effects.
How long does it take for buspirone to take effect?
One of the most common questions is “How long does it take for buspirone to work?” Many patients seek immediate relief, but buspirone requires persistence and patience. Initial improvement can usually be felt after just two weeks of regular treatment. However, the full effect is usually felt after 4–6 weeks.
It is important to remember that how a person feels after two weeks may not reflect the full picture. Even if the medication does not seem to be effective, it is recommended to continue taking it as recommended by your doctor and not to stop on your own. If necessary, your doctor may increase the dosage or decide to switch to another treatment.
Side effects of buspirone (Sorbonne)
Common side effects
- dizziness: Many report feeling "lightheaded," especially during the initial adjustment period.
- NauseaMild nausea often occurs. Taking the medicine with a little food may help.
- Headaches: Some patients experience headaches of varying degrees of severity.
- Fatigue: You may feel tired or slightly dizzy, but in most cases it is not extreme fatigue.
Rare side effects
- Allergic reactions: Itching, skin rash, or shortness of breath require immediate medical attention.
- Mood changes: In very unusual situations, behavioral changes may occur that require a visit to a doctor.
- Feeling of inner restlessness: Some people complain of an inability to physically relax, but this is a less common phenomenon.
Comparison to side effects of other anxiety medications
- Benzodiazepines: May cause severe drowsiness, impaired motor skills, and significant addiction potential.
- SSRIs: May cause a temporary worsening of symptoms at the beginning of treatment, in addition to possible changes in sexual desire.
Buspirone side effects are usually milder. In many cases, they subside and even go away after a short adaptation period.
Is buspirone addictive?
The question "Is buspirone addictive?" often arises. People are familiar with other anti-anxiety medications, mainly from the benzodiazepine family, which are known to have a high risk of physical and psychological dependence. But buspirone (Sorbonne) does not belong to this family.
Low addiction potential
Unlike benzodiazepines, buspirone does not act directly on GABA receptors in the brain. Its mechanism of action produces less of a "high" or momentary euphoria, and therefore does not lead to the development of addiction or dependence to a similar extent. International health organizations also tend to agree that the risk of addiction is significantly lower.
In the context of "is buspirone a controlled substance," the answer is no. In the United States and many other countries, it is not classified as a controlled substance or as a drug with a high risk of abuse. This is a significant advantage for patients who are interested in long-term treatment and do not want to risk addiction.
Withdrawal symptoms
“Buspirone withdrawal” exists as a term, but it usually refers to very mild symptoms. In rare cases, patients report a little anxiety or discomfort when stopping treatment, but this is not a severe withdrawal syndrome, like that known from other drugs. However, it is always a good idea to consult a doctor before stopping treatment, to help with an orderly reduction in dosage, if necessary.
Interactions with other drugs and alcohol
Combination with alcohol
Many people wonder if it is permissible to drink alcohol while taking buspirone. Combining buspirone and alcohol is not recommended. While there is no absolute prohibition like with other medications, alcohol may increase dizziness or fatigue. Furthermore, alcohol can increase anxiety levels in the long term and conflict with medication.
Other possible interactions
- Central nervous system depressants: When combined with narcotics, sleeping pills, or benzodiazepines, increased drowsiness or fatigue may occur.
- CYP3A4 inhibitorsSubstances found in grapefruit juice, some antibiotics, or antifungal medications can inhibit the breakdown of buspirone, leading to an increase in its concentration in the blood.
- Other psychiatric medications: Combination with antidepressants (such as Zoloft) or with antipsychotic medications requires close medical monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between buspirone and xanax?
Xanax (Alprazolam) is a benzodiazepine with a relatively immediate and sedative effect. Buspirone (Sorbonne) is not a benzodiazepine, acts more slowly and is almost non-addictive. However, Xanax may provide rapid relief from an acute anxiety attack. Buspirone, on the other hand, is intended for long-term treatment.
What is the difference between buspirone and zoloft?
Zoloft (Sertraline) is an SSRI, which interferes with the reuptake of serotonin. Buspirone acts as a partial agonist at 5-HT1A receptors and does not belong to the SSRI family. Sometimes, the two drugs are combined together in certain cases of anxiety or depression, but this is under medical supervision.
Does buspirone help with sleep?
The drug is not primarily intended to treat sleep problems. However, some patients do report an overall improvement in sleep quality due to reduced anxiety. If the primary goal is to treat sleep disorders, other medications may be more appropriate.
How is buspirone used to treat anxiety?
The medication should be taken consistently, as directed by your doctor. In most cases, start with a low dose of 5-10 mg per day (buspirone hcl 10 mg) and gradually increase as needed. Do not expect immediate relief. Improvement occurs after several weeks.
How long does buspirone take to work?
In the immediate sense, taking a single dose will not cause an immediate noticeable change like other sedatives. Its effect develops over weeks. Therefore, it is important to continue treatment regularly.
Can I stop buspirone all at once?
In most cases, abruptly stopping buspirone does not cause severe withdrawal symptoms. However, doctors usually recommend gradually reducing the dosage to avoid the risk of a momentary worsening of anxiety.
Is buspirone suitable for every adult?
In most cases, yes. However, you should share your health status and other medications with your doctor. You should monitor for possible side effects. For people with liver or kidney problems, it is advisable to consult about the appropriate dosage.
Is it possible to get generic buspirone?
It can be obtained from various health insurance companies, including Clalit, Maccabi, Meuhedet, and Leumit. In each case, a prescription from a qualified mental health or family medicine physician is required.
Does it also help with depression?
Buspirone can indeed help people with depression combined with anxiety, but usually as a secondary treatment in combination with antidepressants. It is not intended to replace classic antidepressant treatment such as SSRIs or SNRIs.
Is it better than Cipralex?
The comparison depends on the medical diagnosis. Cipralex (Escitalopram) is an effective SSRI for anxiety and depression. Buspirone works by a different mechanism and is used primarily for GAD. Sometimes the two are combined.
Summary
Buspirone (Sorbonne) is a unique medication for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorders. Unlike benzodiazepines, it requires persistence and patience until the full effect is noticeable. However, its great advantage lies in the fact that the potential for addiction is relatively low, and the risk of severe withdrawal symptoms is small.
Many patients are looking for information about buspirone reviews and impressions from people who have used the drug. While some report a significant improvement in anxiety, others wait a relatively long time until they feel a benefit. In any case, it is recommended to act according to the instructions of the attending physician. It should be taken into account that each person reacts differently to the drug.
In terms of dosage (buspirone dosage), it is common to start at 5 or 10 mg per day and progress to 30 mg or more, in divided doses. Side effects such as dizziness, nausea, and headaches should be monitored. These effects are usually mild and go away over time.
It is important to avoid a dangerous combination of buspirone and alcohol, mainly because the combination may increase effects such as dizziness or confusion. Regarding buspirone vs xanax, the main difference is that benzodiazepines are immediately effective but more addictive, while buspirone acts gradually and is considered safer for continuous use.
In conclusion, buspirone (Sorbonne) may be a good choice for patients with GAD who need a long-term solution. However, it is worth remembering that it will not provide immediate relief, and therefore should not be used as an emergency substitute for severe anxiety attacks. Before starting treatment, it is recommended to consult a doctor or pharmacist, and read additional professional information about the drug.

פרופ’ אלון גרין הוא מומחה לפסיכיאטריה קלינית ומחקר תרופתי, עם התמחות בפיתוח והתאמת תרופות מרשם למגוון מצבים נוירו-פסיכיאטריים. בעל ניסיון של למעלה מ־35 שנה בעבודה קלינית ואקדמית, וכיהן כמרצה ופרופסור אורח במספר אוניברסיטאות מובילות בארץ ובחו”ל. עמד בראש יחידות מחקר וטיפול בבתי חולים ציבוריים ומרכזים רפואיים מתקדמים. תחומי עיסוקו כוללים קשב וריכוז (ADHD), הפרעות חרדה והרגעה, דיכאון קליני והפרעות מצב רוח, וכן טיפולים תרופתיים תומכי דיאטה ואיזון מטבולי. משלב גישות מבוססות ראיות עם חדשנות פרמקולוגית, ופרסם עשרות מאמרים מקצועיים בכתבי עת מדעיים, תוך תרומה משמעותית להבנת מנגנוני פעולה של תרופות והשפעתן הקלינית.